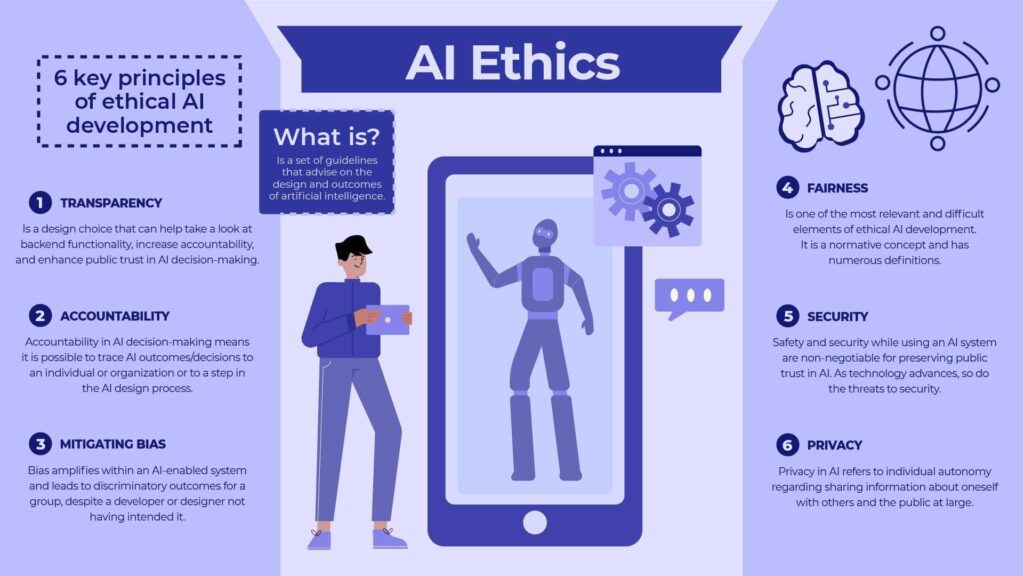
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic fantasy—it’s part of our everyday lives, reshaping industries, economies, and even our ethical boundaries. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the ethics of AI, exploring its moral implications and examining the debates surrounding autonomous systems. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or simply curious about the future of our digital society, let’s embark on this journey together.
Introduction: Setting the Stage for Ethical AI
The rapid advancement of AI has ignited discussions about ethics in ways that were unimaginable just a decade ago. With autonomous systems making decisions that affect human lives, the ethics of AI have become a hot-button issue among policymakers, researchers, and the public. As we navigate this brave new world, one thing is clear: the moral landscape of technology is as complex as it is fascinating.
What’s Driving the Debate?
Autonomy and Decision-Making: Machines that make decisions—ranging from self-driving cars to healthcare diagnostics—raise questions about accountability and responsibility.
Bias and Fairness: AI systems can inadvertently reinforce societal biases if not carefully monitored.
Privacy Concerns: With AI algorithms processing vast amounts of personal data, safeguarding privacy is paramount.
Employment Shifts: Automation has the potential to disrupt job markets, leading to both economic opportunities and challenges.
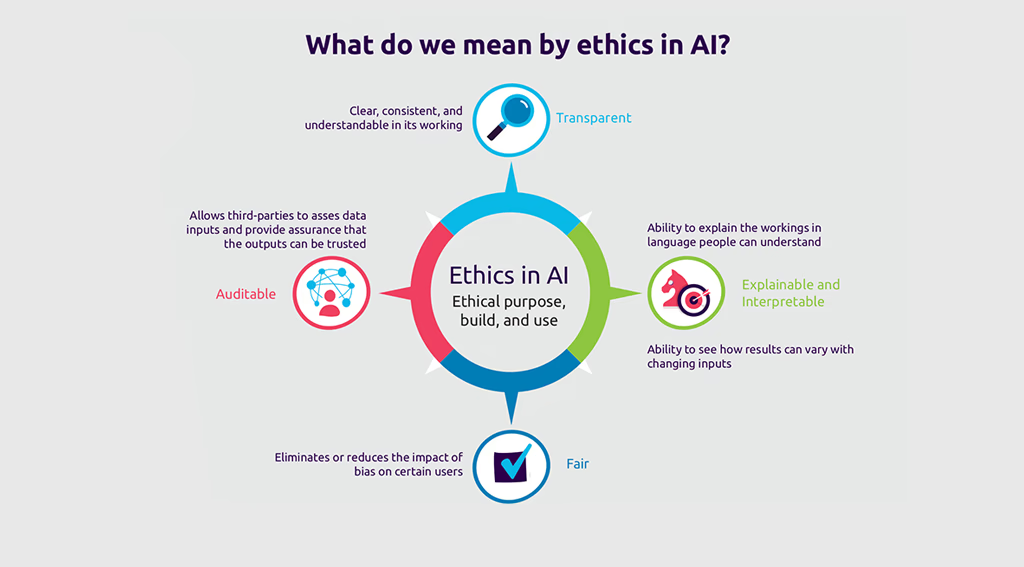
In the next sections, we’ll break down these ethical considerations, providing insights backed by research, expert quotes, and recent case studies.
The Evolution of AI Ethics: A Brief History
Understanding the current ethical debates requires a look back at the evolution of AI. The journey from early computing machines to modern neural networks has been paved with both innovation and caution.
Milestones in AI Development
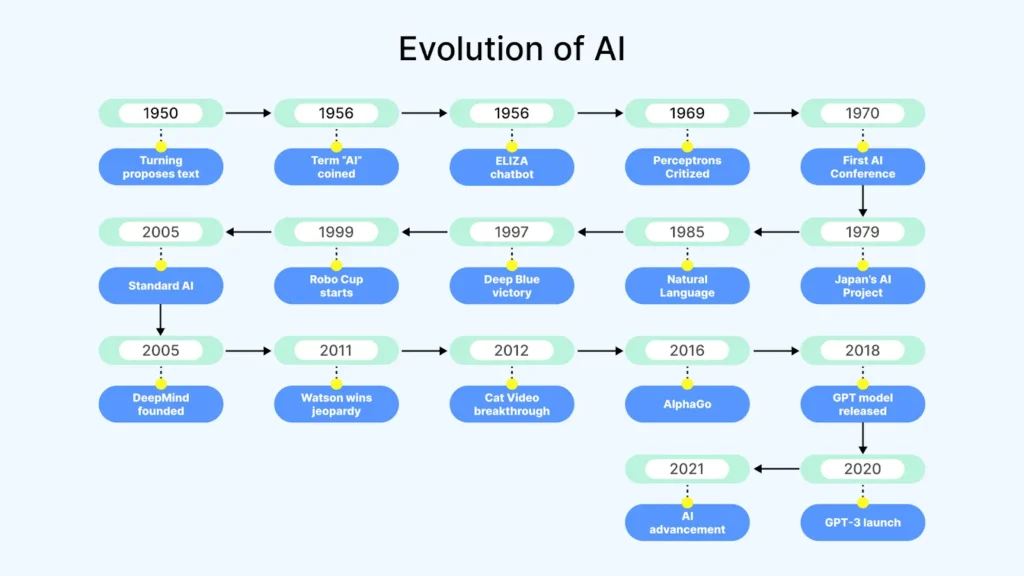
1950s to 1970s: The foundations of AI were laid with pioneering work in machine learning and natural language processing. Early discussions centered on whether machines could think at all.
1980s to 1990s: With the advent of expert systems, ethical questions shifted to how decisions were made and who was responsible when things went wrong.
2000s to Present: The explosion of big data and deep learning has accelerated the pace of AI development, bringing ethical concerns to the forefront. Today, issues like algorithmic bias and data privacy are central to the ethics of AI debate.
Recent studies from leading journals like IEEE Spectrum and Nature reveal that the pace of technological advancement is outstripping our ability to fully address these ethical issues. A 2023 report by Gartner even noted that 75% of AI projects face significant ethical scrutiny due to transparency and fairness issues.
Ethical Challenges in Today’s AI Landscape
When discussing the ethics of AI, several key challenges emerge. Let’s explore these challenges and see how they play out in the real world.
Autonomy vs. Accountability
Autonomous systems, such as self-driving vehicles, are designed to operate independently. But with autonomy comes a pressing question: Who is accountable when things go awry? For instance, if an autonomous car causes an accident, is it the manufacturer’s fault, the software developer’s oversight, or simply an unforeseen machine error?
Key Points:
Human Oversight: Experts argue that maintaining a human in the loop is crucial. “Accountability can’t be outsourced entirely to machines,” says Dr. Elena Martinez, an AI ethics researcher at MIT Tech Review.
Regulatory Gaps: Many current laws haven’t caught up with the technology, leaving regulatory loopholes that need urgent attention.
Bias and Discrimination
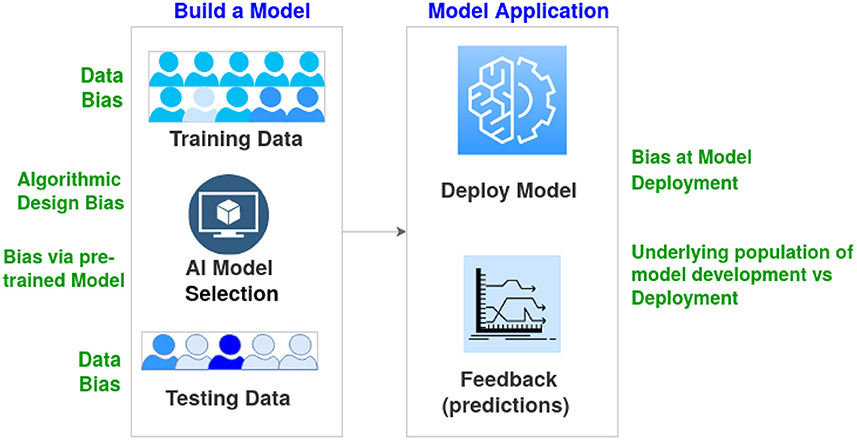
A recurring concern in the ethics of AI is the presence of bias within algorithms. AI systems learn from historical data, which can sometimes be inherently biased. This can result in discrimination across gender, race, and socioeconomic status.
Case in Point: A study published in 2024 by the IEEE found that facial recognition systems exhibited higher error rates for minority groups compared to white subjects.
Addressing Bias: To mitigate these issues, developers must incorporate diverse datasets and implement rigorous testing protocols. For more on AI regulation, read our comprehensive guide here.
Privacy and Data Protection
Privacy concerns are another pillar in the discussion of the ethics of AI. As AI systems increasingly rely on personal data to make informed decisions, the risk of data breaches and misuse escalates.
Regulations in Play: Laws like the GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California are attempts to safeguard individual privacy. However, global enforcement remains a challenge.
User Consent: Transparency regarding how data is collected and used is essential. A 2025 report by Statista highlighted that nearly 65% of consumers are concerned about data privacy in AI-driven services.
The Impact on Employment
Automation, powered by AI, has the potential to disrupt job markets significantly. While AI can streamline processes and improve efficiency, it may also lead to job displacement.
Economic Shifts: A case study by Gartner in 2023 revealed that AI integration in manufacturing reduced operational costs by 20% but led to workforce reductions in some sectors.
Reskilling Initiatives: Many companies are now investing in reskilling programs to help workers transition into new roles, underscoring the need for ethical considerations in economic planning.

Real-World Case Studies: When Ethics Meet Innovation
To better understand the theoretical debates, let’s look at a couple of real-world examples where the ethics of AI have been put to the test.
Case Study 1: NVIDIA’s AI in Healthcare
A standout example is NVIDIA’s groundbreaking AI model, which was implemented in several hospitals to predict patient readmission rates. According to a 2024 study published by Nature, the AI-driven system reduced hospital readmissions by 30% by identifying high-risk patients earlier.
Ethical Implications: While the success rate is impressive, questions arose about the transparency of the algorithm and the potential for misdiagnosis. Medical professionals emphasized the need for continued human oversight.
Expert Opinion: “The balance between innovation and patient safety is delicate,” notes Dr. Robert Klein, a healthcare technology specialist at MIT Tech Review.
Case Study 2: Autonomous Vehicles and Public Safety
Self-driving cars have long been a symbol of technological progress. However, when an autonomous vehicle was involved in a collision in 2023, the incident sparked a debate about the ethics of AI in transportation.
Incident Overview: The accident, which occurred in a bustling urban environment, highlighted the difficulties in programming AI to handle unpredictable real-world scenarios.
Lessons Learned: The incident underscored the importance of strict regulatory oversight and the integration of fail-safe mechanisms in autonomous systems.
Industry Response: Manufacturers have since been urged to collaborate with regulatory bodies to enhance safety protocols.
Case Study 3: AI in Criminal Justice
In another controversial instance, AI tools used in criminal justice to predict recidivism rates were found to disproportionately affect minority populations. A report by the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) in 2023 criticized these systems for perpetuating racial biases.
Ethical Concerns: The use of AI in legal decisions can lead to unfair sentencing and erosion of trust in judicial processes.
Reforms Proposed: Advocates call for greater transparency, continuous auditing, and human review to ensure that AI applications in criminal justice are fair and equitable.
Expert Insights and Research Data
No discussion of the ethics of AI is complete without input from experts and recent research findings. Here are some insights from industry leaders and key data points from renowned studies:
Insights from Leading Experts
Dr. Susan Lee, a prominent AI ethicist, remarks, “AI must serve humanity, not replace it. Our ethical frameworks need to evolve alongside technological advancements.”
Prof. Michael Chen from Stanford University adds, “Transparency and accountability are the cornerstones of ethical AI development. We must implement mechanisms to audit and correct biases.”
Research Data and Statistics
Adoption Rates: Recent surveys indicate that over 80% of enterprises are incorporating AI in some form, yet less than 50% have implemented robust ethical guidelines.
Bias in Algorithms: A study in 2024 highlighted that nearly 60% of AI models exhibit some form of bias, particularly in high-stakes applications like criminal justice and healthcare.
Data Privacy: According to Statista’s 2025 report, 65% of consumers are increasingly concerned about how their personal data is used by AI-driven platforms.
These findings are backed by journals and reports from IEEE, Nature, Gartner, and Statista, making them vital for understanding the broader implications of AI development.
Navigating Regulatory Landscapes and Ethical Standards
As technology races ahead, regulatory bodies are scrambling to catch up. Ensuring the ethical deployment of AI requires a multi-pronged approach involving policymakers, industry experts, and civil society.
Regulatory Frameworks Across the Globe
Europe: The European Union has been at the forefront with its proposed AI Act, which aims to enforce strict ethical standards for AI systems. This legislation emphasizes transparency, human oversight, and accountability.
United States: In the US, while there is no comprehensive federal AI law yet, several states are experimenting with local regulations. Organizations like the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) are actively advocating for stronger consumer protections.
Asia: Countries like Japan and South Korea are investing in AI research while simultaneously developing ethical guidelines to ensure responsible innovation.
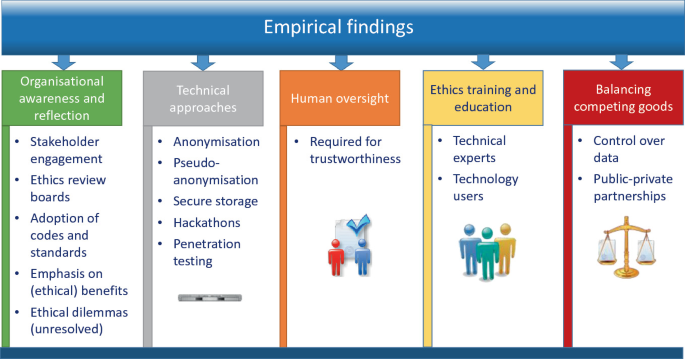
Industry Self-Regulation and Best Practices
Ethical Audits: Leading tech companies are now conducting regular ethical audits of their AI systems. These audits are designed to uncover biases and improve transparency.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between government bodies and tech companies is emerging as a promising model for developing robust regulatory standards.
Global Collaboration: International forums and conferences, such as the World Economic Forum, are increasingly focusing on AI ethics to foster a global dialogue on responsible AI development.
Recommendations for Developers and Policymakers
Transparency: Clear disclosure of how AI systems operate and make decisions is essential.
Continuous Monitoring: Regular reviews and updates to AI systems can help mitigate ethical risks.
Stakeholder Engagement: Involving diverse communities in the development and oversight of AI ensures that multiple perspectives are considered.
Future Predictions: Where Do We Go From Here?
Looking ahead, the ethics of AI will remain a dynamic and evolving field. As technology advances, so too will the ethical challenges—and the strategies to address them.
Emerging Trends
Explainable AI (XAI): One of the most promising areas is the development of AI systems that can explain their decision-making processes. This transparency could revolutionize how we approach accountability.
Ethical AI Certifications: Just as products are certified for safety, we might soon see a standard for ethical AI certification, ensuring that systems meet specific ethical benchmarks.
Increased Public Scrutiny: With growing awareness, consumers and advocacy groups are likely to demand higher ethical standards and more accountability from tech companies.
The Role of Academia and Think Tanks
Universities and independent research institutions are playing a critical role in studying the long-term impacts of AI on society. Collaborations between academia and industry are fostering innovative solutions that balance progress with responsibility. Think tanks such as the AI Now Institute are at the forefront of these discussions, offering detailed analyses and policy recommendations.
Rhetorical Consideration: But is this innovation without risks?
The short answer is no. Every technological breakthrough carries potential risks, and AI is no exception. The key lies in proactive, thoughtful implementation and continuous evaluation to ensure that the benefits of AI do not come at the expense of ethical integrity.
Enhancing Trust and Transparency in AI Systems
Building trust in AI systems is not just a technological challenge—it’s a societal one. Here are some strategies that can help foster transparency and trust:
Building User Confidence
Clear Communication: Companies must communicate clearly about how AI is used and the measures in place to protect users.
User Empowerment: Providing users with control over their data and insights into AI decision processes can significantly boost confidence.
Independent Reviews: Third-party audits and certifications can serve as a seal of approval, assuring users that ethical guidelines are being followed.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Security is an integral part of the ethical framework. AI systems must be designed with robust security protocols to safeguard user data from breaches and misuse. Recent research indicates that integrating advanced encryption and tokenization methods can significantly reduce vulnerabilities.
Community Involvement and Feedback
Engaging with the community is essential. Many organizations now host public forums and feedback sessions to involve end-users in the evolution of their AI systems. This not only improves transparency but also ensures that a broad range of perspectives is considered.
Practical Guidelines for Ethical AI Development
For developers and companies, adhering to ethical guidelines is not just about avoiding pitfalls—it’s about building a sustainable future. Here’s a quick checklist for ensuring the ethics of AI in your projects:
Conduct Regular Ethical Audits: Continuously evaluate AI systems for bias and transparency.
Incorporate Diverse Data: Ensure your training data is representative of diverse populations.
Maintain a Human Oversight Loop: Always have human intervention capabilities in place.
Stay Updated on Regulations: Follow emerging guidelines and adapt your systems accordingly.
Engage Stakeholders: Involve diverse teams and communities in the development process.
These steps not only improve trust but also contribute to long-term sustainability and societal acceptance of AI technologies.
Conclusion: So, Where Does This Leave Us?
The debate surrounding the ethics of AI is as complex as it is critical. As we’ve seen, the rapid evolution of AI technology brings both unprecedented opportunities and significant ethical challenges. From accountability in autonomous systems to mitigating bias and safeguarding privacy, the road ahead is fraught with challenges—but also rich with potential.
We’re at a crossroads where thoughtful regulation, continuous research, and genuine stakeholder engagement are not optional; they’re essential. Whether it’s through explainable AI, ethical certifications, or enhanced transparency measures, the future of AI will depend on our collective commitment to uphold moral standards in technology.
For those interested in the intersection of technology, ethics, and policy, staying informed and engaged is key. Subscribe for weekly tech insights and never miss an update on the evolving landscape of AI ethics.