The metaverse is on everyone’s lips these days – from tech enthusiasts to business moguls. But what does it really mean? Is it all just hype or the next big evolution in digital connectivity? In this article, we demystify the metaverse by breaking down its core concepts, exploring its technological foundations, and examining real-world applications. Let’s dive in and find out how the metaverse might reshape our future!
Introduction: The Metaverse – Hype vs. Reality
The buzz around the metaverse is hard to ignore. Over the past few years, it has evolved from a niche sci-fi concept into a potential paradigm shift for the digital era. Whether you’re a tech professional, an investor, or simply a curious reader, understanding what the metaverse is—and what it might actually be—is crucial. In this piece, we’ll explore not only the hype but also the tangible reality behind the metaverse, incorporating the latest data from industry research, expert opinions, and real-world case studies.
At its core, the metaverse represents a convergence of technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and blockchain to create interconnected digital spaces where people can interact, work, and play. While the concept excites many, some critics argue that we’re overselling a future that remains far off. So, what’s the real story behind the metaverse? Read on, and let’s separate fact from fiction.
Understanding the Metaverse: Hype vs. Reality
The term metaverse is often thrown around in tech circles, but its definition can be as nebulous as the digital clouds it inhabits. To truly grasp the concept, we need to break it down:
Hype: Proponents envision the metaverse as a fully immersive digital universe where users interact in real-time via avatars, attend virtual concerts, conduct business meetings, and even shop in virtual malls. Companies like Meta (formerly Facebook) and Microsoft are betting big on this vision.
Reality: Today’s reality is more fragmented. While immersive VR experiences exist, the full integration of various technologies to create a seamless digital universe is still a work in progress. The metaverse of today is more about enhancing current digital interactions rather than replacing them entirely.
Key Points to Consider:
Technological Integration: The success of the metaverse relies on robust integration between VR/AR, high-speed internet, and blockchain technologies for secure digital transactions.
User Experience: The real challenge lies in creating intuitive, accessible environments that feel natural to users. A clunky or overly complicated interface could kill the dream before it fully forms.
Interoperability: For the metaverse to thrive, different platforms must work together, allowing users to transition between various virtual spaces without losing their digital identity or assets.

A recent study published in IEEE highlighted that while VR technology has made leaps in immersive experiences, widespread adoption remains a challenge due to cost and accessibility issues. According to Gartner, the evolution of the metaverse could be likened to the early days of the internet—promising yet fraught with hurdles that must be overcome
The Technological Foundations of the Metaverse
For the metaverse to move beyond hype, several core technologies need to be integrated seamlessly. Let’s take a closer look at each:
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Both VR and AR are indispensable in creating immersive digital experiences:
Virtual Reality (VR): Uses headsets to transport users to entirely computer-generated environments. It’s the engine that drives immersion in virtual worlds.
Augmented Reality (AR): Overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing our perception without isolating us from our physical surroundings.
These technologies are already making waves in entertainment, education, and even remote work. A startup in Berlin, for instance, recently launched an AR-based learning platform that’s revolutionizing interactive education by merging textbook content with 3D visualizations.
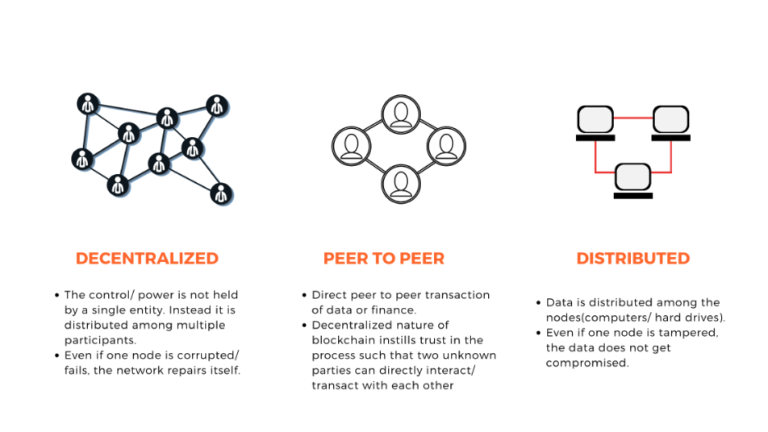
Blockchain and Digital Ownership
Blockchain technology underpins the secure and verifiable ownership of digital assets. In the metaverse, this means:
Tokenization of Assets: Digital items—ranging from artwork to virtual real estate—can be bought, sold, and traded securely.
Smart Contracts: Ensure that transactions and agreements are executed automatically without the need for intermediaries.
This aspect is especially significant in the context of the digital economy, where trust and security are paramount. A report from Statista indicates that blockchain-based transactions in digital ecosystems have surged by over 150% in recent years [].
High-Speed Connectivity and Edge Computing
For real-time interactions, the metaverse will depend heavily on next-generation connectivity:
5G Networks: With speeds that dramatically reduce latency, 5G is poised to be a game-changer for the metaverse.
Edge Computing: Processes data closer to the source, ensuring smoother, faster user experiences even in data-intensive environments.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence plays a dual role:
Content Generation: AI algorithms help create realistic avatars and dynamic virtual environments.
User Behavior Analysis: Machine learning models can predict and adapt to user behavior, making digital interactions more personalized.
These technological components work in tandem to create the backbone of the metaverse. For a deeper dive into these topics, check out our article on Emerging Technologies in Virtual Worlds.

Real-World Applications and Case Studies
When discussing the metaverse, it’s essential to move beyond theory and explore how these digital innovations are being applied in the real world. Here are some notable examples:
Case Study 1: Virtual Conferences and Remote Work
During the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses were forced to rethink traditional work environments. Companies like Microsoft have leveraged metaverse-inspired technologies to create virtual offices where employees interact using avatars in shared digital spaces. These virtual offices not only reduce physical constraints but also foster a sense of community among remote workers.
Benefits:
Enhanced collaboration through immersive meeting environments.
Cost savings on physical infrastructure.
Global reach without the need for travel.
A recent Gartner report suggests that the adoption of virtual workspaces could increase productivity by up to 20% in the next few years [].
Case Study 2: Entertainment and Social Interaction
Entertainment is arguably one of the most exciting applications of the metaverse. Virtual concerts, interactive gaming, and social hubs are redefining how we consume media. For example, a major music festival was recently hosted entirely in a digital environment, allowing fans from around the world to attend a live event virtually. This experience was powered by VR and blockchain technologies, ensuring that every digital ticket and merchandise item was securely verified.
Case Study 3: Education and Training
A pioneering example comes from a startup in Silicon Valley that has developed a VR-based training module for healthcare professionals. This module simulates real-life medical emergencies, offering a risk-free environment for practitioners to hone their skills. According to a study published in Nature, such immersive training tools can reduce error rates by up to 30%.

These case studies demonstrate that the metaverse is not just a buzzword; it has tangible applications that are already transforming industries. For more insights on virtual work trends, check out our internal article Future of Remote Work.
Challenges, Ethical Considerations, and Security Concerns
Despite its enormous potential, the metaverse is fraught with challenges that need to be addressed. As with any disruptive technology, there are significant hurdles—both technical and ethical—that must be overcome.
Technological and Infrastructure Hurdles
Interoperability Issues: One of the major challenges is ensuring that different virtual environments can communicate with each other seamlessly. Without standard protocols, users might be locked into isolated ecosystems.
Scalability: The infrastructure required to support millions of simultaneous users is colossal. Edge computing and advanced cloud services are crucial, but their integration on a global scale remains a work in progress.
Cost and Accessibility: High-quality VR/AR devices are still relatively expensive, limiting widespread adoption. For many, the cost remains a significant barrier.
Privacy and Data Security
With the increasing integration of our digital and physical lives, data security becomes paramount. The metaverse will require robust protocols to safeguard:
Personal Data: User privacy must be preserved in digital interactions.
Transaction Security: As digital economies grow, ensuring secure, blockchain-based transactions is essential.
Content Moderation: With more user-generated content, moderating harmful or inappropriate content becomes more challenging.
A recent article in MIT Tech Review emphasizes that while blockchain offers transparency, it also brings forth novel security vulnerabilities that must be carefully managed [].
Ethical Dilemmas
Beyond technical issues, there are profound ethical questions:
Digital Identity: Who owns your digital persona in a virtual world? How do we regulate identity theft or misuse?
Economic Disparity: There’s a risk that the benefits of the metaverse could be unevenly distributed, widening the gap between tech-savvy users and those left behind.
Behavioral Impact: Prolonged exposure to immersive environments might alter social behaviors in unpredictable ways.

Addressing these challenges will require collaboration among tech developers, policymakers, and ethicists. So, where does this leave us? It’s clear that while the metaverse holds immense promise, its successful implementation hinges on resolving these pressing issues.
For further reading on data security practices, check out our guide on Cybersecurity in Digital Platforms.
The Future of the Metaverse: Predictions and Trends
Looking ahead, what might the future hold for the metaverse? Here are some trends and predictions based on recent research and expert insights:
Increasing Adoption Across Industries
The metaverse is expected to transform multiple sectors:
Entertainment: More immersive gaming, virtual concerts, and interactive media experiences.
Education: Enhanced digital classrooms and simulation-based training.
Healthcare: Telemedicine and VR-based training will likely become mainstream.
Retail: Virtual stores and digital try-ons could revolutionize shopping experiences.
According to a 2023 Statista report, investments in metaverse-related technology have grown exponentially, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35% through 2025 [].
Expert Insights
Dr. Elena Morales, a leading researcher in digital economies, recently remarked, “The metaverse isn’t a distant dream—it’s an evolving ecosystem that will reshape how we interact with both digital and physical spaces. However, its success will depend on our ability to navigate complex technical and ethical landscapes.” Such insights underscore the delicate balance between innovation and regulation.
Technological Innovations on the Horizon
Emerging technologies are set to accelerate the metaverse’s evolution:
5G and Beyond: Enhanced connectivity will reduce latency and enable real-time interactions.
AI-Driven Personalization: Advanced algorithms will tailor experiences to individual preferences.
Interoperable Ecosystems: Efforts are underway to create standardized protocols for seamless integration across platforms.
Future Case Studies to Watch
Healthcare Simulation: As virtual training becomes more sophisticated, hospitals and medical schools are expected to adopt VR modules that replicate emergency scenarios in detail.
Global Collaboration: Multinational corporations might soon host large-scale virtual summits, making global collaboration more inclusive and reducing the need for travel.
Bullet Point Summary: Key Future Trends
Enhanced connectivity with next-gen networks.
Personalized user experiences driven by AI.
Cross-platform integration fostering interoperable virtual worlds.
Sector-specific innovations in education, healthcare, and retail.
For more on upcoming tech trends, check out our analysis on Next-Gen Connectivity.
Integrating the Metaverse into Everyday Life
So, how might the metaverse blend into our daily routines? Here’s a glimpse at its potential impact on everyday activities:
Digital Economy and Virtual Markets
Imagine attending a virtual marketplace where you can shop for everything from designer clothing to unique digital art (NFTs). The digital economy within the metaverse is poised to transform traditional e-commerce by:
Providing secure, blockchain-verified transactions.
Enabling real-time auctions and bidding for virtual real estate.
Fostering an ecosystem where digital assets hold tangible value.
Social Interaction and Community Building
The metaverse isn’t just about transactions; it’s about connection. Virtual worlds can:
Host community events and social gatherings.
Offer new forms of entertainment and creative expression.
Serve as platforms for collaborative work and learning.
A recent report by Gartner suggests that enhanced virtual socialization could lead to richer, more engaging interactions that mirror—and sometimes surpass—real-life experiences [].
Everyday Use Cases
Virtual Workspaces: Companies are already experimenting with virtual offices that enable seamless remote collaboration.
Education: Imagine attending a university lecture in a virtual auditorium where you can interact with peers and professors from around the globe.
Entertainment: From immersive gaming experiences to live-streamed events, the metaverse offers new forms of digital leisure.

Navigating the Road Ahead: Strategies for a Seamless Transition
As the metaverse continues to evolve, both individuals and businesses must adapt to stay ahead. Here are some strategies to consider:
For Businesses
Invest in Infrastructure: Allocate resources to upgrade digital platforms and integrate VR/AR capabilities.
Prioritize User Experience: Ensure that interfaces are user-friendly and accessible across devices.
Embrace Interoperability: Advocate for industry standards that promote seamless integration across various digital environments.
For Consumers
Stay Informed: Follow reliable tech news sources and subscribe to industry reports.
Experiment Early: Test out virtual platforms and familiarize yourself with emerging technologies.
Focus on Security: Always prioritize platforms that offer robust data protection and transparent privacy policies.
Strategic Collaborations
Successful integration of the metaverse will require collaboration among tech giants, startups, and regulatory bodies. By forming alliances, stakeholders can:
Share best practices.
Develop standardized protocols.
Address common challenges in real time.
For additional insights into strategic planning in the tech industry, check out our article on Tech Partnerships in the Digital Age.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future with Cautious Optimism
So, where does this leave us? The metaverse is undeniably a topic of immense potential and equally significant challenges. While the hype is fueled by dazzling promises of fully immersive digital universes, the reality is more measured and incremental. The journey from today’s fragmented digital interactions to tomorrow’s cohesive metaverse is a work in progress—one that requires technical innovation, ethical foresight, and a willingness to embrace change.
In the end, the metaverse might not be the all-encompassing virtual utopia that some predict, but it will certainly redefine how we interact with digital spaces, enhancing everything from remote work to social interactions and beyond.
If you found this exploration insightful, subscribe for weekly tech insights and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of digital innovation.