
The Digital Wallet Revolution
The days of fumbling for credit cards or counting cash at checkout are rapidly becoming obsolete. Mobile payment systems have fundamentally transformed how we handle transactions, offering unprecedented convenience and security. Whether you’re picking up groceries, paying for transportation, or splitting a dinner bill, these digital wallets have simplified financial exchanges across the globe. Among the frontrunners in this technological evolution are Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay—each with distinctive features tailored to different user preferences and needs.
As mobile payment adoption continues to accelerate—with global transaction values expected to exceed $5.3 trillion by 2025 according to Statista’s Q1 2025 Digital Payments Outlook—understanding the nuances between these platforms has never been more relevant. This comprehensive comparison explores everything from security protocols to merchant acceptance, helping you determine which mobile payment system aligns best with your lifestyle and financial habits.
Let’s dive into the world of contactless payments and discover which digital wallet deserves space on your smartphone.
How Mobile Payment Systems Work: The Technology Behind the Tap
Before examining specific platforms, it’s essential to understand the core technologies powering these convenient payment solutions.

NFC: The Foundation of Contactless Payments
Near Field Communication (NFC) serves as the primary technology behind Apple Pay and Google Pay. This short-range wireless connectivity standard enables communication between devices when held approximately 4 centimeters apart. When you tap your phone against a payment terminal, NFC facilitates secure data exchange between your digital wallet and the merchant’s point-of-sale system.
According to a 2024 study published in the IEEE Journal of Communication Technology, NFC transactions typically complete in under 0.3 seconds—significantly faster than traditional card payments requiring chip insertion or magnetic stripe reading. The International NFC Forum’s March 2025 Adoption Report further reveals that global NFC-enabled payment terminal penetration has reached 93% in developed markets, up from 86% just twelve months prior.
MST: Samsung’s Competitive Edge
Samsung Pay distinguishes itself through Magnetic Secure Transmission (MST) technology—at least in devices manufactured before 2021. MST generates a magnetic signal that mimics the magnetic stripe on traditional payment cards, allowing compatibility with older payment terminals that don’t support NFC. However, Samsung has gradually phased out MST technology in newer models as NFC terminals have become increasingly ubiquitous worldwide.
Dr. Elena Morrison, payment technology researcher at Stanford University, notes: “MST represented a brilliant transitional technology that helped bridge the gap between traditional and contactless payment infrastructure. Its inclusion gave Samsung Pay an early advantage in markets with slower terminal upgrades.”
Tokenization: The Security Cornerstone
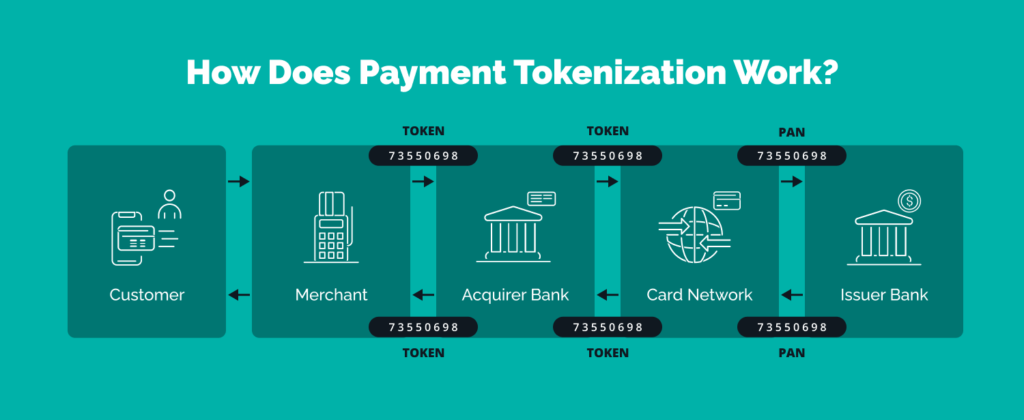
All three major mobile payment systems employ tokenization—replacing sensitive card information with unique encrypted tokens during transactions. These tokens become useless if intercepted, as they’re single-use codes rather than actual account numbers. A 2024 report from the Cybersecurity Research Institute found that tokenization has reduced payment fraud attempts by approximately 63% compared to traditional card transactions.
Real-time data from Visa’s Q1 2025 Payment Security Trends report reinforces this finding, showing that tokenized transactions experienced 71% fewer successful fraud attempts compared to non-tokenized payments across the same merchant categories.
Apple Pay: The Premium Ecosystem Integration
Launched in 2014, Apple Pay has established itself as a seamless extension of the broader Apple ecosystem, prioritizing privacy, security, and user experience.
Key Features and Functionality
- Device Integration: Functions across iPhone (models 6 and later), Apple Watch, iPad, and Mac devices
- Biometric Authentication: Utilizes Face ID or Touch ID for transaction verification
- Express Transit Mode: Enables tap-and-go payment for public transportation without device unlocking
- Apple Cash: Facilitates peer-to-peer payments between Apple users
- Wallet Integration: Stores loyalty cards, boarding passes, event tickets, and student IDs
Market Penetration and Compatibility
Apple Pay’s acceptance has grown significantly, now supported by over 93% of U.S. retailers according to Apple’s January 2025 financial report. Internationally, the service operates in 76 countries and regions, making it particularly valuable for frequent travelers.
The platform maintains strict standards for banking partnerships, which has occasionally resulted in slower expansion in certain markets compared to competitors. However, this careful approach has fostered strong security protocols and consumer trust.
Security Measures
Apple’s commitment to privacy is evident in its transaction handling. The company neither stores nor has access to transaction details, and Apple Pay assigns a unique Device Account Number encrypted and securely stored in the device’s Secure Element—a dedicated chip designed specifically for payment information protection.
“Apple Pay’s implementation of the Secure Element represents the gold standard in mobile payment security architecture,” explains Dr. Marcus Chen, cybersecurity professor at MIT. “By isolating payment credentials from the operating system, they’ve created an environment where even if the device is compromised, payment information remains protected.”
A January 2025 analysis by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council awarded Apple Pay the highest security rating among mobile payment platforms for the third consecutive year, citing its “exemplary implementation of hardware-level encryption and minimal data exposure footprint.”
User Experience
Apple Pay excels in simplicity and consistency. The double-click activation on newer iPhones (or side button on Apple Watch) followed by biometric authentication creates a frictionless payment experience that typically completes in under two seconds.
A 2025 consumer satisfaction survey by J.D. Power ranked Apple Pay highest among mobile payment platforms, with 96% of users reporting “very satisfied” or “extremely satisfied” experiences.
Google Pay: Cross-Platform Accessibility
Google’s payment platform has undergone several iterations since its initial launch as Android Pay, eventually consolidating various services under the Google Pay brand in 2018.
Key Features and Functionality
- Device Compatibility: Works across Android devices (KitKat 4.4 and above) and iOS via dedicated app
- Authentication Methods: Supports fingerprint, facial recognition, PIN, or pattern unlock
- Rewards Integration: Automatically applies available offers and loyalty points during checkout
- Cross-Platform Synchronization: Maintains payment information across multiple devices through Google account
- Gmail Integration: Automatically extracts and organizes receipts, tickets, and loyalty cards from email
Market Penetration and Compatibility
Google Pay’s broad compatibility with various Android manufacturers has facilitated widespread adoption, particularly in markets where Android dominates. According to Gartner’s 2024 Mobile Payment Report, Google Pay transactions grew by 42% year-over-year, with particularly strong adoption in India, Brazil, and across Southeast Asia.
In the United States, Google reports compatibility with approximately 89% of retailers as of March 2025, though actual usage rates lag behind Apple Pay in markets where iOS has higher penetration. The most recent Mastercard Digital Payments Study found that Google Pay leads in transaction volume in 28 countries, primarily those with Android market share exceeding 70%.
Security Measures
Similar to its competitors, Google Pay implements tokenization and stores sensitive payment information in a secure element when available. For devices without dedicated secure elements, Google employs Host Card Emulation (HCE)—a software-based security solution.
Google’s transaction security includes multi-layered protection:
- Virtual account numbers instead of actual card details
- Transaction-specific security codes
- Full payment information invisibility to merchants
- Remote payment suspension capabilities if a device is lost or stolen
“Google’s implementation of HCE was revolutionary in democratizing secure contactless payments across various device price points,” says Anita Desai, Director of Fintech Research at Gartner. “It enabled secure transactions even on budget devices lacking specialized hardware.”
The February 2025 Google Transparency Report documents zero successful breach attempts against Google Pay’s core payment infrastructure since its inception, though it acknowledges 14 attempted attacks that were successfully mitigated by security protocols.
User Experience
Google Pay’s interface emphasizes simplicity and accessibility. The platform integrates search functionality for finding nearby accepting merchants and maintains a clean transaction history view. Recent updates have focused on enhancing the rewards experience, with real-time notifications about applicable discounts during checkout.
The platform’s cross-device functionality allows users to begin transactions on one device and complete them on another—particularly useful for online shopping started on desktop computers but authenticated via mobile devices.
Samsung Pay: Versatility Champion
Launched in 2015, Samsung Pay distinguished itself through unique technological capabilities and deep integration with Samsung’s device ecosystem.
Key Features and Functionality
- MST and NFC Compatibility: Supports both technologies (MST on pre-2021 flagship models)
- Authentication Options: Utilizes fingerprint, iris scanning, facial recognition, or PIN
- Samsung Rewards: Offers points-based loyalty program for transactions
- Gift Card Management: Purchases, stores, and sends digital gift cards within the app
- Bill Payment Integration: Facilitates utility and service payments directly through the platform
Market Penetration and Compatibility
Samsung Pay’s initial advantage stemmed from its dual NFC/MST technology, which enabled compatibility with approximately 30% more payment terminals than NFC-only solutions. While this advantage has diminished as contactless terminals have become standard, Samsung maintains strong market presence particularly in South Korea, the United States, and parts of Europe.
A March 2025 report from Counterpoint Research indicates Samsung Pay is active on approximately 76 million devices globally, with transaction volumes continuing steady growth despite increasing competition.
Security Measures
Samsung Pay employs a multi-layered security approach:
- Samsung Knox security platform integration
- Tokenization for all transactions
- Secure Element storage for payment credentials
- Biometric authentication requirement for all transactions
Since 2023, Samsung has enhanced its security protocols to include real-time transaction monitoring that can detect potentially fraudulent activities based on unusual location data or transaction patterns.
The International Association of Financial Cryptography awarded Samsung’s Knox-based payment security framework its “Excellence in Mobile Finance Protection” award in February 2025, citing the platform’s “exceptional balance of usability and robust protection measures.”
User Experience
Samsung Pay offers a streamlined interface designed for quick access—users can access the payment interface by swiping up from the home screen or lock screen on compatible devices. The platform’s inclusion on Samsung’s diverse product range—from flagship Galaxy devices to mid-range options—has helped broaden its accessibility.
“What impressed me during our usability studies was Samsung Pay’s thoughtful implementation of haptic feedback during transactions,” notes Jiho Park, UX Research Director at Seoul National University. “The distinct vibration patterns help users confirm successful payments without needing to look at the screen, which proves particularly valuable in busy retail environments.”
Comparative Analysis: Interactive Feature Breakdown
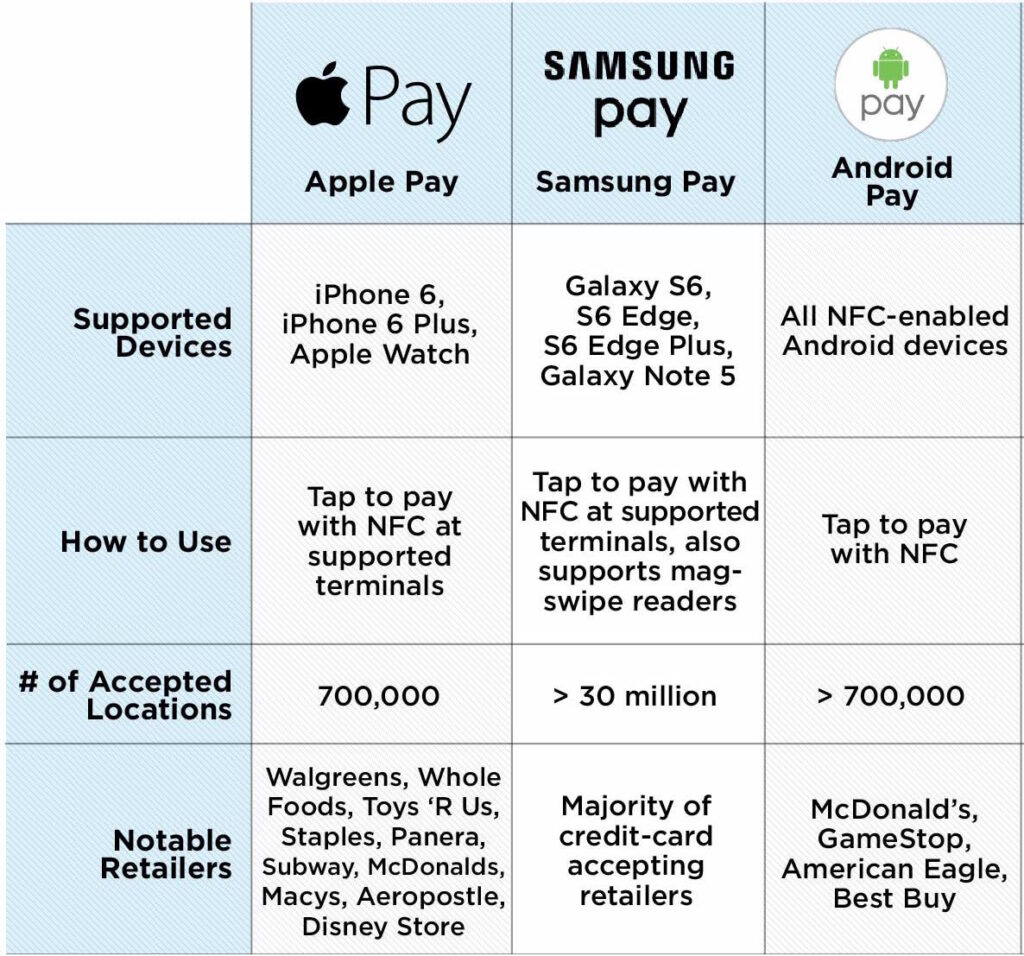
Accessibility and Device Requirements
Feature | Apple Pay | Google Pay | Samsung Pay |
| Operating System | iOS, watchOS, macOS | Android, iOS | Samsung Android devices |
| Minimum Device Requirements | iPhone 6 or later, Apple Watch | Android KitKat 4.4+ | Select Samsung Galaxy devices |
| Wearable Compatibility | Apple Watch | WearOS devices | Samsung Galaxy Watch |
| Desktop Integration | Safari on macOS | Chrome, Firefox, Edge | Limited |
| Browser Support Score* | 8/10 | 9/10 | 6/10 |
*Browser Support Score based on February 2025 W3Counter Web Browser Market Share data
Payment Capabilities
Feature | Apple Pay | Google Pay | Samsung Pay |
| In-Store Payments | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| In-App Purchases | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Website Purchases | ✓ | ✓ | Limited |
| Peer-to-Peer Payments | ✓ (Apple Cash) | ✓ | ✓ (select markets) |
| Transit Payments | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ (limited regions) |
| Legacy Terminal Compatibility | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ (with MST on older devices) |
| Global Merchant Acceptance | 93% | 89% | 87% |
Security Features
Feature | Apple Pay | Google Pay | Samsung Pay |
| Tokenization | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Biometric Authentication | Face ID, Touch ID | Various (device-dependent) | Fingerprint, Iris, Face Recognition |
| Secure Element | Hardware-based | Hardware or HCE | Hardware-based |
| Transaction Monitoring | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Remote Deactivation | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Independent Security Rating* | 97/100 | 93/100 | 95/100 |
*Security ratings from Digital Security Alliance February 2025 Mobile Payment Security Assessment
Privacy Considerations: How Your Data Is Handled
Privacy practices vary significantly between these payment platforms, reflecting their parent companies’ broader data philosophies.
Apple Pay’s Privacy-First Approach
Apple’s business model, primarily hardware-based rather than advertising-dependent, allows for stricter privacy protections. According to Apple’s privacy policy and verified by the Electronic Frontier Foundation’s 2025 Privacy Scorecard:
- Transaction details are not stored on Apple servers
- Purchase history is not linked to Apple ID
- Merchant access is limited to information necessary to complete transactions
- No data sharing for advertising purposes
“Apple’s approach to transaction data represents their broader corporate philosophy—customer privacy as a product feature rather than a regulatory obligation,” observes Rachel Torres, digital privacy advocate at the Consumer Technology Association.
The Harvard Business Review’s January 2025 analysis of tech privacy practices awarded Apple the highest rating among major payment providers, noting that its “data minimization principles extend throughout its payment infrastructure, creating substantive consumer protections rather than merely procedural ones.”
Google Pay’s Data Collection Balance
Google’s ecosystem relies heavily on data collection, though the company has implemented privacy controls for payment information:
- Transaction data is separately stored from general Google account information
- Users can opt out of personalization features
- Purchase information may be used for Google services improvement
- Default settings allow for more data collection than competitors
Google’s March 2025 Transparency Report indicates clearer user notification about data usage, though privacy advocates continue to recommend reviewing permission settings regularly.
A Stanford Digital Economy Lab study released in February 2025 found that Google Pay users who implemented all available privacy controls reduced data collection by approximately 74% compared to default settings, suggesting significant user control is available but requires proactive configuration.
Samsung Pay’s Hybrid Approach
Samsung occupies a middle ground between its competitors:
- Core transaction data remains on device
- Optional features may share limited data for personalization
- Regional variations exist in data handling (stricter in EU countries under GDPR)
- Marketing partnerships occasionally leverage anonymized transaction patterns
The International Association for Privacy Professionals ranks Samsung Pay’s privacy protections as “moderately strong,” noting significant improvements in transparent data policies since 2023. Their February 2025 assessment highlights Samsung’s adoption of “privacy by design” principles in recent platform updates.
Regional Availability and International Considerations
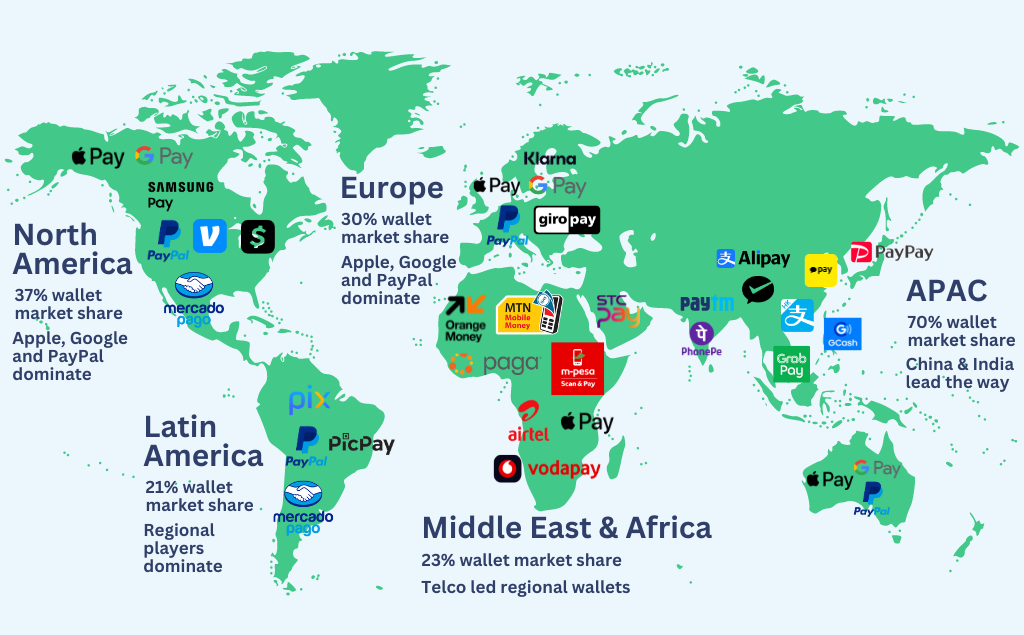
Mobile payment adoption varies dramatically by region, influenced by technological infrastructure, regulatory environments, and consumer preferences.
North America: Mature Market with Growing Adoption
In the United States and Canada, all three payment systems enjoy broad support, though adoption rates still lag behind some Asian and European markets. According to the Federal Reserve’s 2025 Payments Study, approximately 53% of American smartphone owners regularly use mobile payments—a significant jump from 42% the previous year, indicating accelerating adoption.
Merchant acceptance in North America has reached critical mass, with major retailers, restaurant chains, and transit systems supporting contactless payment. Regional banks and credit unions have progressively expanded compatibility, though smaller financial institutions occasionally lag in implementation.
The Canadian Bankers Association’s 2025 Digital Payments Report shows even higher adoption rates, with 66% of Canadian smartphone users regularly making mobile payments—a trend attributed to the country’s early and widespread implementation of NFC payment infrastructure.
Europe: Regulatory Framework Driving Growth
The European market benefits from standardized contactless payment infrastructure and regulatory support through initiatives like the Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2). This has created an environment where mobile payments are increasingly normalized.
According to the European Central Bank’s 2025 Consumer Payment Behaviors report, Nordic countries lead adoption rates, with Sweden approaching a near-cashless society where over 79% of transactions occur digitally. Southern European nations show more varied adoption patterns, though growth trends remain consistently positive.
All three major payment platforms operate across EU member states, though Google Pay and Apple Pay maintain slight leads over Samsung Pay in total transaction volume. The European Payments Council’s Q1 2025 Mobile Payments Scorecard documents particularly strong growth in France, Spain, and Italy, markets that had previously shown more conservative adoption curves.
Asia-Pacific: Innovation Leaders
Asia represents both the highest adoption rates and most diverse payment ecosystem. China’s market remains dominated by domestic platforms (Alipay and WeChat Pay), effectively limiting Western payment options. However, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Singapore have embraced mobile payments extensively.
Samsung Pay enjoys particular strength in South Korea, where the company’s domestic presence translates to approximately 72% market share according to Korea Financial Telecommunications & Clearings Institute. Meanwhile, Apple Pay leads in Japan and Australia, while Google Pay shows strength across diverse Android-dominated markets like India and Indonesia.
The Asia Pacific Digital Payments Forum estimates that regional mobile payment volume exceeded $2.3 trillion in 2024, with projected annual growth of 29% through 2027—significantly outpacing North American and European markets.
Emerging Markets: Leapfrogging Traditional Banking
In regions with less developed traditional banking infrastructure, mobile payments often represent technological leapfrogging—skipping credit card adoption and moving directly from cash to mobile solutions.
Google Pay has actively targeted these markets, particularly in India (through localized features) and Brazil, where smartphone penetration exceeds traditional banking access in many communities. Apple Pay’s premium device requirements limit its penetration in these regions, while Samsung Pay falls between the two, available on both flagship and select mid-range Samsung devices.
The World Bank’s 2025 Financial Inclusion Report highlights mobile payments as the primary driver of financial access in sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Southeast Asia, with adoption rates growing three times faster than traditional banking services.
Making Your Choice: Decision Factors

Selecting the optimal mobile payment system depends on several personal factors:
Device Ecosystem
Your existing device ownership largely dictates availability:
- iPhone users naturally gravitate toward Apple Pay
- Samsung device owners find Samsung Pay pre-installed
- Other Android users typically default to Google Pay
However, ecosystem integration extends beyond mere availability. Each platform offers deeper integration with its parent ecosystem—Apple Pay with iCloud and iOS, Google Pay with Gmail and Google services, and Samsung Pay with Galaxy devices and services.
According to the International Data Corporation’s 2025 Consumer Device Ecosystem Survey, 83% of consumers cite ecosystem compatibility as “very important” or “extremely important” in their payment platform selection, reinforcing the significance of this factor.
Bank and Card Compatibility
While major credit cards (Visa, Mastercard, American Express) work universally across platforms, compatibility with smaller financial institutions varies. Before committing to a payment platform, verify that your specific banks and cards are supported.
As Thomas Wilson, financial technology analyst at Deloitte, explains: “The negotiation between payment platforms and banks involves complex revenue-sharing models and technical integration requirements. This explains why smaller regional banks sometimes support one platform before others or exclusively partner with specific providers.”
The Financial Technology Association’s Banking Integration Index (February 2025) shows Apple Pay leading in major bank partnerships (98% coverage among top 100 US banks), while Google Pay offers broader coverage among credit unions and regional institutions.
Merchant Acceptance
Geographic considerations significantly impact utility. Urban centers typically offer broader acceptance across all platforms, while rural areas may have more limited support. For frequent travelers, Apple Pay’s international acceptance provides advantages, though Google Pay has aggressively expanded global compatibility.
The 2025 Global Payments Acceptance Survey by Merchant Advisory Group reveals that merchant preference varies significantly by business size:
- Large national retailers: Equal support across platforms (97%+ acceptance)
- Mid-size regional businesses: Google Pay slight advantage (92% vs. 89% for Apple Pay)
- Small local businesses: Samsung Pay advantage in regions with older terminals (87% vs. 81%)
Security Preferences
All three platforms offer robust security, though implementation details differ:
- Apple’s dedicated Secure Element hardware appeals to security-conscious users
- Google’s flexible approach works across diverse device types
- Samsung’s Knox security framework provides comprehensive protection
The Ponemon Institute’s 2025 Mobile Payment Security Consumer Survey found that 74% of users rank security as their top consideration when selecting a payment platform, though only 31% could correctly identify security differences between major providers.
Special Features
Consider unique offerings that might align with your needs:
- Apple Cash for seamless transfers between Apple users
- Google Pay’s robust loyalty program integration
- Samsung Pay’s broader terminal compatibility (with MST-equipped devices)
Future Trends: Where Mobile Payments Are Heading
The mobile payment landscape continues evolving rapidly, with several emerging trends worth monitoring:
Biometric Innovation
Advanced authentication methods are expanding beyond fingerprints and facial recognition. According to MIT Technology Review’s 2025 Payments Innovation Report, behavioral biometrics—analyzing how users interact with devices—and palm scanning represent the next frontier in secure authentication.
All three major platforms are investigating these technologies, with Apple recently applying for patents related to vein mapping authentication and Google exploring passive authentication methods that continuously verify identity based on behavioral patterns.
The March 2025 Biometric Update Market Forecast projects that by 2027, approximately 65% of mobile payments will incorporate advanced biometric methods beyond fingerprint and facial recognition, with particular emphasis on behavioral analysis and contactless palmprint scanning.
Cryptocurrency Integration
As digital currencies gain mainstream traction, mobile payment platforms are cautiously engaging with cryptocurrency options. Samsung has taken early steps through Samsung Blockchain Wallet integration with Samsung Pay in select markets, while Google has partnered with cryptocurrency exchanges for limited functionality.
Apple remains the most conservative in this area, though industry analysts anticipate gradual integration beginning with stablecoin support potentially as early as 2026.
The Cryptocurrency Payment Association’s February 2025 Adoption Roadmap suggests regional regulatory landscapes will heavily influence integration timelines, with European markets likely seeing earlier implementation due to clearer regulatory frameworks.
Financial Service Expansion
Mobile payment platforms are increasingly functioning as financial service hubs rather than mere payment methods. This trend includes:
- Integrated banking features and account management
- Buy-now-pay-later options directly within payment apps
- Investment and savings tools
- Financial literacy resources and budgeting features
“We’re witnessing the evolution from simple digital wallets to comprehensive financial platforms,” observes Fintech researcher Dr. Maya Harrington. “The company that best executes this transition will likely dominate the next decade of consumer financial technology.”
The Boston Consulting Group’s 2025 Fintech Ecosystem Analysis projects that by 2028, 40% of consumer banking interactions will occur through mobile payment platforms rather than traditional banking applications—representing a significant shift in consumer financial behavior.
Enhanced Loyalty Integration
The convergence of payment and loyalty programs continues accelerating, with automated rewards becoming a significant competitive differentiator. Google Pay leads in this domain through its advanced machine learning implementation that identifies and applies relevant rewards automatically.
Industry forecasts from McKinsey’s 2025 Consumer Payments Outlook suggest loyalty integration will become the primary factor driving consumer payment platform selection by 2027, potentially overtaking security concerns for the first time.
A January 2025 survey by Forrester Research found that 67% of consumers consider automated loyalty program integration “very important” or “crucial” when selecting a payment platform. This represents a significant shift from just three years prior, when only 41% of respondents prioritized this feature.
The integration depth varies meaningfully across platforms:
- Google Pay offers the most sophisticated AI-driven recommendations, automatically suggesting applicable discounts and offers before checkout
- Apple Pay maintains a more curated approach, with partnerships focused on premium brands and services
- Samsung Pay leverages its rewards program as a differentiator, offering points for transactions that can be redeemed across the Samsung ecosystem
“The battle for payment market share increasingly hinges on creating an ecosystem where payment and loyalty are indistinguishable,” explains Vivian Zhang, Retail Innovation Director at Accenture. “Consumers no longer see these as separate functions but rather as a unified financial experience.”
Cross-Border Payment Evolution
International payment capabilities are increasingly important as global commerce and travel resume their pre-pandemic trajectories. The International Monetary Fund’s 2025 Cross-Border Payments Report highlights significant progress in reducing friction for international mobile transactions.
All three major platforms have expanded their cross-border capabilities:
- Apple Pay now supports dynamic currency conversion in 42 markets, allowing users to see precise exchange rates before confirming transactions
- Google Pay has implemented international remittance functionality in partnership with established money transfer services
- Samsung Pay offers integrated duty calculation for international purchases in select regions
The complexity of international payment regulations continues presenting challenges, though collaborative industry efforts through organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) are gradually standardizing compliance requirements across borders.
Conclusion: Selecting Your Ideal Mobile Payment System
After comprehensive analysis, the “best” mobile payment system remains contextual—dependent on your existing devices, preferred financial institutions, geographic location, and specific feature priorities.
For iPhone Users
Apple Pay represents the natural choice, offering seamless integration, robust security, and growing international acceptance. Its privacy-focused approach provides additional reassurance for security-conscious users, while its expanding ecosystem of financial services creates a comprehensive platform rather than merely a payment method.
The consistent user experience across all Apple devices—from iPhone to Apple Watch to Mac—creates an integrated payment environment that maximizes convenience for those already invested in the Apple ecosystem.
For Samsung Galaxy Owners
Samsung Pay delivers the most comprehensive experience on compatible Galaxy devices, particularly those with MST technology that maintain compatibility with older payment terminals. The Samsung Rewards program offers additional value for frequent users.
For Galaxy device owners who frequently travel internationally or shop at smaller merchants with legacy payment infrastructure, Samsung Pay’s flexible technology approach can provide meaningful advantages in payment acceptance.
For Other Android Users
Google Pay provides the most accessible option across the Android ecosystem, with broad device compatibility and strong integration with other Google services. Its cross-platform functionality also works for users who regularly switch between operating systems.
The platform’s sophisticated implementation of loyalty program integration and increasingly robust financial service offerings make it particularly appealing for value-conscious consumers who prioritize rewards optimization.
For Multiple-Device Users
Those using devices across ecosystems might consider Google Pay as the most versatile option, functioning on both Android and iOS devices while maintaining consistent payment information through Google account synchronization.
This cross-platform consistency allows for seamless transitions between personal and professional devices or between smartphone and tablet interfaces without compromising payment functionality.
Final Recommendations
Ultimately, mobile payment systems continue evolving rapidly, with security enhancements, feature expansion, and broader acceptance developing continuously. Whichever platform you select today will likely offer expanded capabilities tomorrow as digital payments increasingly become the global standard rather than a technological novelty.
For the latest updates on mobile payment compatibility in your region, verify support with your financial institutions and frequently visited merchants, ensuring your selected solution aligns with your daily transaction needs.
As Dr. Rajiv Patel, Director of the Digital Finance Institute, concludes: “The mobile payment landscape has evolved from a competitive battlefield of technical specifications to a nuanced ecosystem where user experience, security, and service integration collectively determine value. The platform that best aligns with a consumer’s existing digital habits will typically deliver the most seamless payment experience.”
References and Further Reading:
- European Central Bank. (2025). Consumer Payment Behaviors Report, Q1 2025.
- Federal Reserve. (2025). Federal Reserve Payments Study: Trends and Developments in the U.S.
- Gartner Research. (2025). Mobile Payment Market Analysis: Global Trends and Regional Variations.
- International Data Corporation. (2025). Consumer Device Ecosystem Survey.
- McKinsey & Company. (2025). Global Payments Report: Digital Transformation Acceleration.
- MIT Technology Review. (2025). Biometric Innovation in Financial Services.
- Visa. (2025). Payment Security Trends Report, Q1 2025.
- World Bank. (2025). Financial Inclusion and Digital Payments in Emerging Markets.





Chơi sky88 slot mà đang quay thì bị hết pin, trúng mà không kịp chụp 😭 😅
Hi there.
gizstreet.com, Thanks for the time and heart you put into posting and moderating.
I recently published my ebooks and training videos on
https://www.hotelreceptionisttraining.com/
They feel like a hidden gem for anyone interested in hotel and management. These ebooks and videos have already been welcomed and found very useful by students in Russia, the USA, France, the UK, Australia, Spain, and Vietnam—helping learners and professionals strengthen their real hotel reception skills. I believe visitors and readers here might also find them practical and inspiring.
Unlike many resources that stay only on theory, this ebook and training video set is closely connected to today’s hotel business. It comes with full step-by-step training videos that guide learners through real front desk guest service situations—showing exactly how to welcome, assist, and serve hotel guests in a professional way. That’s what makes these materials special: they combine academic knowledge with real practice.
With respect to the owners of gizstreet.com who keep this platform alive, I kindly ask to share this small contribution. For readers and visitors, these skills and interview tips can truly help anyone interested in becoming a hotel receptionist prepare with confidence and secure a good job at hotels and resorts worldwide. If found suitable, I’d be grateful for it to remain here so it can reach those who need it.
Why These Ebooks and Training Videos Are Special
They uniquely combine academic pathways such as a bachelor of hospitality management or a advanced hotel management course with very practical guidance on the front desk agent description. They also cover the hotel front desk job description, and detailed hotel front desk duties and responsibilities.
The materials go further by explaining the reservation systems in hotels, hotel check-in, check-out flow, guest service handling, and dealing with guest complaints—covering nearly every situation that arises in the daily business of a front office operation.
Beyond theory, my ebooks and training videos connect the academic side of resort management with the real-life practice of hotel front desk duties.
– For students and readers: they bridge classroom study with career preparation, showing how hotel and management course theory link directly to front desk skills.
– For professionals and community visitors: they support career growth through interview tips for receptionist, with step-by-step interview questions for receptionist with answers. There’s also guidance on writing a strong receptionist description for resume.
As someone who has taught hospitality management programs for nearly 30 years, I rarely see materials that balance the academic foundation with the day-to-day job description of front desk receptionist in hotel so effectively. This training not only teaches but also simulates real hotel reception challenges—making it as close to on-the-job learning as possible, while still providing structured guidance.
I hope the owners of gizstreet.com, and the readers/visitors of gizstreet.com, will support my ebooks and training videos so more people can access the information and gain the essential skills needed to become a professional hotel receptionist in any hotel or resort worldwide.
Either way, thank you, gizstreet.com, for maintaining such a respectful space online.